You can purchase domains within Route 53 or register domains that have been purchased elsewhere. In Figure 12.2, you can see a domain search being performed in the AWS Management Console.
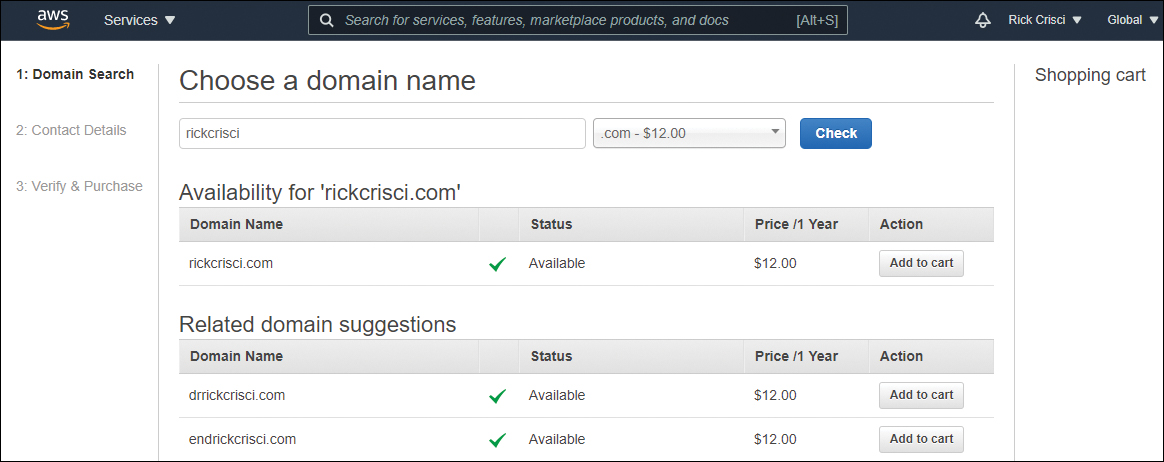
FIGURE 12.2 Registering a domain
After the domain is registered, you can configure DNS. In Figure 12.3, you can see the NS records for the purchased domain, as well as an alias record pointed to an Elastic Load Balancer (ELB). This means that when someone on the Internet resolves the address rickcrisci.link, the traffic is directed to the ELB.
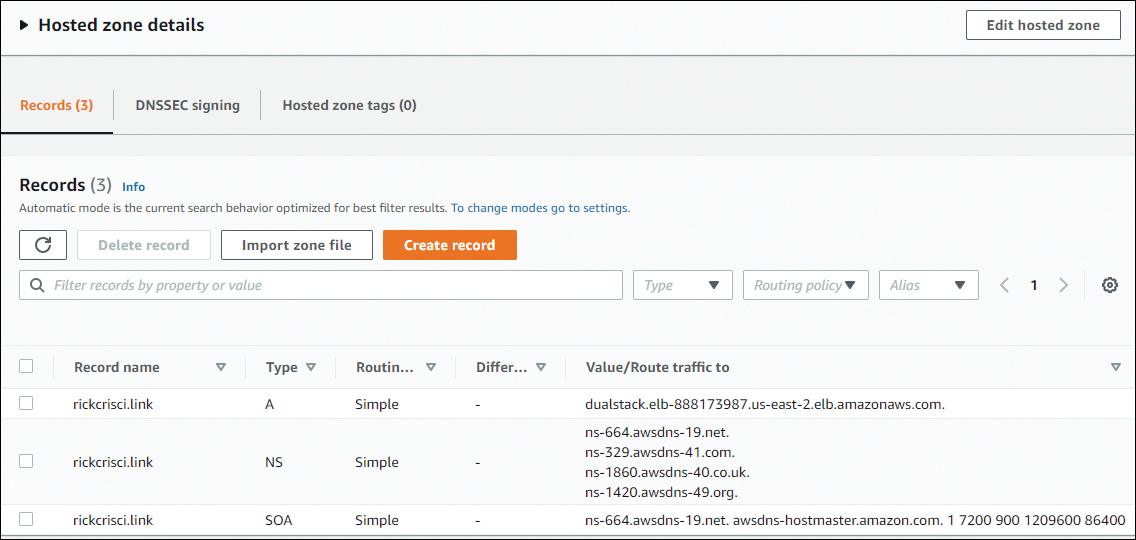
FIGURE 12.3 Public hosted zone
An alias record is a DNS record type that is unique to Route 53. An alias record is used to forward traffic to an AWS service, such as a CloudFront distribution, an Elastic Load Balancer, or an S3 bucket. You can create an alias record at the zone apex. For example, if you register the domain rickcrisci.link, the zone apex is rickcrisci.link. There may also be subdomains (mobile.rickcrisci.link). Creating an alias record allows you to point the zone apex to another name instead of an IP address. You cannot create a CNAME record for the zone apex.
An alias record can be used at the domain apex (such as example.com) or on subdomains. A CNAME record can be used on subdomains (such as mobile. example.com). An alias record can point to AWS services like CloudFront or an Elastic Load Balancer.
Answer these questions. The answers follow the last question. If you cannot answer these questions correctly, consider reading this section again until you can.
1. Your organization has multiple AWS accounts for different purposes. You use a dedicated account to manage all Route 53 configurations including domains and public hosted zones. There is also a different AWS account in which an auto scaling group of web servers runs behind an Internet-facing ELB. How can you configure Route 53 to send all traffic for example.com to the web servers?
A. This configuration is possible only if you configure Route 53 and the ELB in the same AWS account.
B. Configure an A record in Route 53 pointed to the IP address of the ELB in the other AWS account.
C. Configure a CNAME record in Route 53 pointed to the ELB in the other AWS account.
D. Configure an alias record in Route 53 pointed to the ELB in the other AWS account.
2. You have an RDS instance running in AWS account #1. A new application is being deployed in a new VPC within AWS account #2. A Route 53 private hosted zone exists in AWS account #1. What must be done to allow the VPC in AWS account #2 to be associated with the private hosted zone? (Choose two.)
A. Create a VPC peering connection.
B. Authorize the association between the private hosted zone in account #1 and the VPC in account #2.
C. Run a command to create the association between the private hosted zone in account #1 and the VPC in account #2.
D. Configure a public hosted zone that will be available to both VPCs.